Constructing and Commercialising Technology: best engineering colleges in bangalore
Innovation is the driving force behind technological progress, and the journey from idea to commercial success requires a structured approach. Constructing a technology involves the design and development of a product or service, while commercialization focuses on taking that technology to market. This guide covers the entire process, from ideation to funding to scaling, along with insights into key agencies and programs that support technology commercialization.
Part 1: Constructing a Technology
The construction phase is where the spark of an idea is transformed into a tangible product or service. This process requires technical skills, creativity, and a clear understanding of market needs. Let’s break down the steps involved in constructing a technology.
Step 1: Identify a Problem or Opportunity
Every successful technology begins with identifying a problem or unmet need. This might come from personal experience, market trends, industry pain points, or emerging opportunities. To identify a problem worth solving:
- Market Research: Conduct thorough research to understand industry trends, customer behaviours, and existing solutions. This helps validate whether there’s a genuine need for your technology.
- Customer Feedback: Engage with potential users to gather insights into their challenges and preferences.
- Competitor Analysis: Study existing competitors to understand their strengths and weaknesses. This can reveal gaps or areas for improvement.
Step 2: Conceptualise the Solution
With a clear problem in mind, the next step is to brainstorm and conceptualise a solution. This phase involves creativity and a clear vision for the technology. Key activities include:
- Brainstorming: Gather a team of diverse experts to generate ideas and explore innovative approaches.
- Define the Core Features: Determine the key functionalities that will differentiate your technology from others.
- Create a Roadmap: Outline the steps to take the concept from idea to prototype. This roadmap serves as a guide throughout the development process.
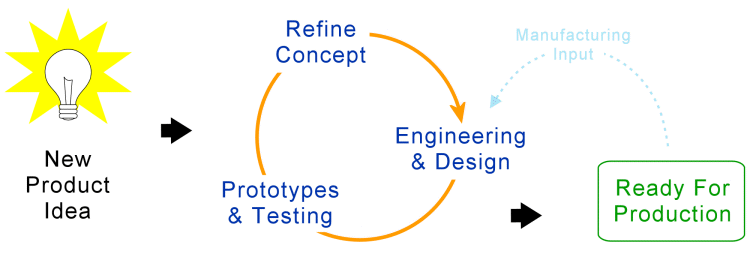
Step 3: Design and Develop the Prototype
Once the concept is established, it’s time to create a prototype—a preliminary model that demonstrates the technology’s functionality. This stage involves:
- Technical Design: Use engineering and design skills to create detailed schematics, blueprints, or code. Tools like Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software are invaluable for this process.
- Prototype Construction: Build the prototype, ensuring it aligns with the concept and intended functionality. This may involve hardware, software, or a combination of both.
- Testing and Iteration: Test the prototype to identify any issues or areas for improvement. Gather feedback from colleagues, industry experts, and potential users, then iterate accordingly.
Step 4: Secure Intellectual Property (IP) Rights
To protect your technology from unauthorised use, securing intellectual property rights is crucial. Patents are the most common form of IP protection for technology. The steps to secure a patent include:
- Patent Search: Conduct a thorough patent search to ensure your technology is unique and doesn’t infringe on existing patents.
- Draft and File a Patent Application: Work with a patent attorney to draft and submit a patent application. This process involves describing the invention in detail and defining the patent claims.
- Monitor and Enforce IP Rights: Once the patent is granted, monitor for potential infringements and take legal action if necessary.
Step 5: Refine the Prototype and Prepare for Production
As you secure IP rights, continue refining the prototype to ensure it’s ready for production. Focus on:
- Design for Manufacturability: Optimise the design for efficient production. Consider materials, manufacturing processes, and cost efficiency.
- Quality Assurance and Compliance: Implement rigorous testing and quality assurance processes to ensure the technology meets industry standards and safety regulations.
Part 2: Commercialising a Technology
Commercialization is the process of taking your technology to market and generating revenue. It requires a strategic business plan, funding, and effective marketing. Let’s explore the key steps involved in commercialization.
Step 1: Develop a Business Plan
A comprehensive business plan is essential for commercialization. It serves as a roadmap for your business and is critical for attracting investors and stakeholders. Key components of a business plan include:
- Executive Summary: A concise overview of your business, including the technology, target market, and unique value proposition.
- Market Analysis: A detailed analysis of the market, including customer demographics, industry trends, and competitor analysis.
- Revenue Model: Define how your business will generate revenue. This could be through product sales, subscriptions, licensing, or other business models.
- Marketing Strategy: Outline how you plan to promote and sell the technology. This includes pricing, distribution channels, and promotional activities.
- Operations and Logistics: Describe your production processes, supply chain, and distribution methods.
- Financial Projections: Provide detailed financial forecasts, including projected expenses, revenues, and break-even analysis.
Step 2: Secure Funding
Commercialization often requires significant funding, and there are various sources to explore. Here’s an overview of common funding sources for technology commercialization:
India offers a variety of funding agencies and programs to support technological commercialization, catering to startups, innovators, and research-based projects. Here are some key agencies:
Department of Science and Technology (DST)
The DST is a leading government body that supports scientific research and innovation. It offers programs such as:
- National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations (NIDHI): Aimed at nurturing innovation and entrepreneurship, NIDHI provides seed funding, incubation, and acceleration support.
- Technology Development Board (TDB): TDB funds projects with commercial potential and promotes the application of technology for societal benefits.
Department of Biotechnology (DBT)
DBT supports biotechnology-based startups and research. It offers funding through:
- Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC): BIRAC provides grants, loans, and equity-based funding to biotech startups and entrepreneurs.
Atal Innovation Mission (AIM)
Part of NITI Aayog, AIM promotes innovation and entrepreneurship. It supports incubators, accelerators, and startup funding through the Atal Tinkering Labs and Atal Incubation Centers.
Indian Angel Networks and Venture Capital Firms
While not government agencies, India has a vibrant network of angel investors and venture capitalists that provide funding and mentorship to startups in technology and related fields.
Incubators and Accelerators
These organisations provide resources, mentorship, and networking opportunities to startups. They often offer seed funding to help startups grow.
Crowdfunding
Platforms like Kickstarter and Indiegogo allow startups to raise funds from the public. This approach is particularly useful for consumer-focused technologies.
Step 3: Establish Partnerships and Collaborations
Partnerships and collaborations can play a significant role in successful commercialization. They can provide additional resources, expertise, and market access. Consider the following:
- Academic Collaborations: Universities and research institutions often have expertise and facilities that can support technology development and testing.
- Industry Partnerships: Partner with established companies in related fields for joint ventures, licensing agreements, or co-marketing initiatives.
- Incubators and Accelerators: These organisations offer mentorship, resources, and networking opportunities, often in exchange for equity or a fee.
Step 4: Launch and Market the Technology
With funding and partnerships in place, you’re ready to launch your technology. This step involves creating a comprehensive launch strategy and executing effective marketing campaigns. Key considerations include:
- Product Launch Strategy: Plan a strategy that includes press releases, product demonstrations, launch events, and other promotional activities.
- Digital Marketing: Leverage digital platforms like social media, email marketing, and online advertising to reach a broader audience.
- Public Relations and Media: Engage with industry publications and media outlets to generate buzz around your technology.
- Customer Support and Feedback: Provide excellent customer support and actively seek customer feedback to improve the product and enhance user satisfaction.
Step 5: Scale and Expand
After a successful launch, focus on scaling your business and expanding your market reach. This step requires operational scalability and strategic planning. Consider the following:
- Operational Scalability: Ensure your production and distribution processes can handle increased demand. This may require expanding facilities or automating certain processes.
- Market Expansion: Explore new geographic regions or customer segments to grow your business.
- Product Diversification: Consider developing new products or services based on your existing technology or leveraging related technologies to diversify your product portfolio.
Conclusion
In our experience at RRCE we believe that both constructing and commercialising technology carry an equal essence and thus use all your bandwidth to work on both no matter how challenging it might be it will be a rewarding journey. It requires a combination of technical expertise, business acumen, and strategic planning. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can increase the chances of successfully turning your innovative idea into a profitable business.
Throughout this journey, leveraging funding opportunities and establishing partnerships with key stakeholders can be crucial. By identifying the right funding agencies and building strong collaborations, you can overcome many of the challenges associated with technology commercialization. Remember, successful commercialization often requires flexibility and adaptability, so be open to refining your strategy as you learn from customer feedback and market trends.



